Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
We measured plasma reflection of densely electron-excited sapphire, quartz, and pylex. The reflectivity shows a maximum 10 ps after the electron-excitation, and a oscillation with a period of about 40 ps. This result will be caused by a coupling between plasma reflection and lattice vibration.
Tsutsui, Kenji; Toyama, Takami*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
no journal, ,
We discuss the electronic states and the resonant X-ray scattering spectra on the high-Tc cuprates with Ni impurities by cluster calculations. In particular, we simulate the spectra in case that the density of doped holes are larger than that of the Ni impurities.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Goto, Jun*; Matsuki, Seishi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Moribayashi, Kengo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Zn
Zn
Kaneko, Koji; Yoshiuchi, Shingo*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Settai, Rikio*; Onuki, Yoshichika
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shiga, Motoyuki; Fujisaki, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
In this paper, I propose a first-principles computational approach to obtain chemical reactions of quantum many-body systems by the extension of Fukui's intrinsic reaction coordinate. For a chemical process from the reactant to the product, we search for a path that passes a barrier in which quantum mechanical free energy is minimum. This opens a way to a first-principles analysis of proton transfer reactions of complex hydrogen bonded systems that involve large amplitude thermal and quantum fluctuations.
Yuri, Yosuke; Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Ishibori, Ikuo; Okumura, Susumu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Narumi, Kazumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Kawase, Keigo*; Mori, Michiaki; Kando, Masaki; Koga, J. K.; Bulanov, S. V.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Minami, Yasuo*; Takei, Ryota*; Onishi, Ryo*; Ishino, Masahiko; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Terakawa, Kota*; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
no journal, ,
To improve the femtosecond laser processing technique more accurate and controllable, the knowledge about the laser ablation process is important. In order to understand the dynamics of the femtosecond laser ablation process, we performed a pump and probe reflectivity imaging of the platinum surface during the femtosecond laser ablation by using the laser-driven soft X-ray laser as a probe beam. The fluence dependence of the soft X-ray reflectivity is classified into three regions: (1) strongly excited, (2) moderately excited, and (3) weakly excited regions. In strongly excited region, the rapid reduction of the reflectivity due to the explosive evaporation in the ablation process of the material surface was observed. In the moderately excited region, the reflectivity reduction is far slower than that in the strongly excited region.
 states in even-even actinide nuclei
states in even-even actinide nucleiAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Sato, Tetsuya; Nagame, Yuichiro; Sato, Nozomi; Ishii, Tetsuro
no journal, ,
Energies of the first-excited states in even-even actinide nuclei were determined precisely through high-resolution  -particle measurements and
-particle measurements and  -
- coincidence measurements. Those energies were measured for a total of 8 isotopes in Pu, Cm, Cf and Fm, and dependences of those energies on the proton and neutron numbers were systematically clarified. It was found that the energy of the first-excited state takes the minimum around Cm and Cf isotopes, and increases with increasing atomic number. This trend was qualitatively explained by taking account of the existence of the spherical closed shell at the proton number
coincidence measurements. Those energies were measured for a total of 8 isotopes in Pu, Cm, Cf and Fm, and dependences of those energies on the proton and neutron numbers were systematically clarified. It was found that the energy of the first-excited state takes the minimum around Cm and Cf isotopes, and increases with increasing atomic number. This trend was qualitatively explained by taking account of the existence of the spherical closed shell at the proton number 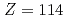 . It was also found that the first-excited state takes the local minimum at
. It was also found that the first-excited state takes the local minimum at  Fm, which clearly indicates the existence of the doubly deformed shell gaps at
Fm, which clearly indicates the existence of the doubly deformed shell gaps at 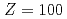 and
and 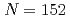 .
.
Metoki, Naoto; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Sakai, Hironori; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Ikeda, Shugo*
no journal, ,
US shows CEF at low temperatures, while magnetic quasi-elastic scattering with increasing temperature. The crossover of 5f character would be the origin for the unusual metal-insulator crossover. We found that the static susceptibility can be well reproduced from the Kramars-Kronnig transformation of our neutron inelastic data. It means (1) no remarkable excitation above 12 meV, (2) the local susceptibility is dominant because of the weak magnetic correlation, and (3) we can estimate the contribution to the static susceptibility from the localized and itinerant part. Localized model is a good approximation and asymptotic limit for low temperatures.
shows CEF at low temperatures, while magnetic quasi-elastic scattering with increasing temperature. The crossover of 5f character would be the origin for the unusual metal-insulator crossover. We found that the static susceptibility can be well reproduced from the Kramars-Kronnig transformation of our neutron inelastic data. It means (1) no remarkable excitation above 12 meV, (2) the local susceptibility is dominant because of the weak magnetic correlation, and (3) we can estimate the contribution to the static susceptibility from the localized and itinerant part. Localized model is a good approximation and asymptotic limit for low temperatures.
Fukaya, Yuki; Maekawa, Masaki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi; Yoshino, Tatsuro*; Saito, Eiji; Kawasuso, Atsuo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Shinichiro; Sai, Hitoshi*; Oshima, Takeshi; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Shimazaki, Kazunori*; Kondo, Michio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otobe, Tomohito
no journal, ,
We simulate the high-harmonic generation in a diamond under intense laser field solving time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation with real-time and -space method. The computational results show that the HHG spectra above the band gap has broad peak. We also find the blue shift of the fundamental and the HHG after the optical breakdown.
Ikeda, Takashi; Hou, Z.*; Wang, X.*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Miyata, Seizo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Minato, Futoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 B flow
B flowMiyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
Reduced fluid models are widely used for nonlinear simulations of magnetised fusion plasmas. Traditionally they are derived from more rigorous fluid model such as the Braginskii model by imposing assumptions like low frequency perturbations. In the traditional derivation, calculation of the gyroviscosity is needed and it is very complicated. Alternatively reduced fluid models can be derived from fluid moment equations of reduced kinetic models. We can bypass the calculation of the gyroviscosity in the alternative method. Recently we derived a reduced kinetic model for plasmas with large E B velocity. Based on the reduced kinetic model, reduced fluid equations are derived and the gyroviscous force is obtained by comparing the reduced equations and fluid equations without reduction.
B velocity. Based on the reduced kinetic model, reduced fluid equations are derived and the gyroviscous force is obtained by comparing the reduced equations and fluid equations without reduction.
 Si
Si , 2
, 2Inami, Toshiya; Ishii, Kenji; Jarrige, I.; Mitsuda, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English